Xanthan Gum - Malaysia
|
Origin |
: Malaysia |
|
IUPAC Name |
: - |
|
Cas Number |
: 11138-66-2 |
|
HS Code |
: 3913.90.20.15 |
|
Formula |
: C35H49O29 |
Basic Info
|
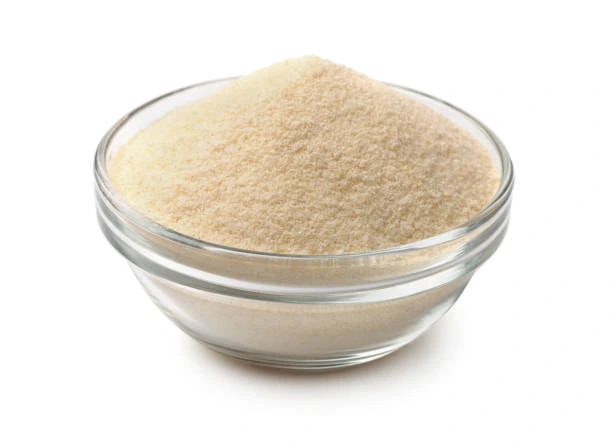
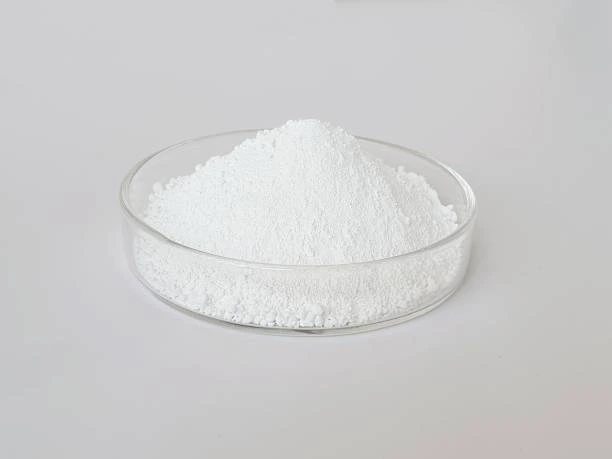
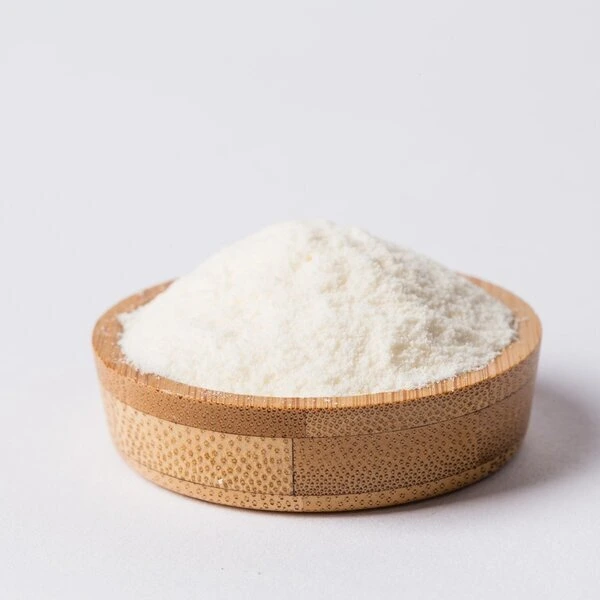
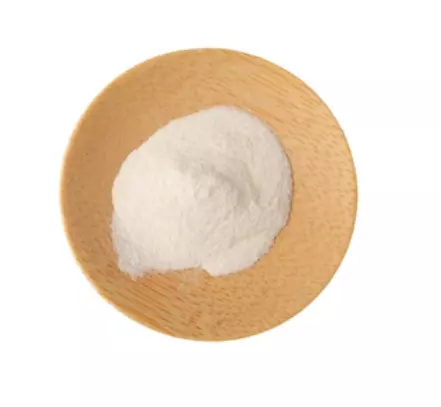
Appearance Name |
: Off white powder |
|
Common Names |
: Corn Sugar Gum |
|
Packaging |
: 25kg/bag |





 English
English
 Indonesian
Indonesian
 简体字
简体字
 العربية
العربية
 Español
Español
 Français
Français
 Português
Português
 日本語
日本語
 한국어
한국어
 Tiếng Việt
Tiếng Việt
